The United States and Qatar are duking it out for supremacy in the global liquefied natural gas (LNG) market. While Qatar’s star is rising, American producers have a few aces up their sleeves that could give them an edge.
America and Qatar each have a 20% share of the 400 million tons a year LNG market. Australia is the other major exporter, but it is likely at or near its peak output due to gas reserve issues and growing domestic demand. Russia, meanwhile, had grand ambitions – and the vast reserves to fulfill them – but sanctions have crippled its prospects.
To be sure, Qatar is a formidable opponent. Blessed with huge, low-cost gas reserves from its giant offshore North Field, the small country approved expansion projects in 2022 that will boost LNG output by 64% – or 49 million tons annually – to 126 million tons annually by 2027.
Qatar Energy is a state-owned entity, so it doesn’t have the same concerns about bureaucratic delays and regulatory red tape that bog down Western companies.
Qatar Energy CEO Saad al-Kaabi said recently that the company would sign a record number of LNG supply deals this year, having already inked two big ones with firms in China and Bangladesh. Al-Kaabi, who also serves as Qatar’s Minister of Energy, claims that about 40% of the new global LNG supply will come from Qatar by 2029.
However, the United States is also experiencing a significant surge in LNG export capacity. It’s just not drawing the same attention as Qatar’s.
The United States began exporting LNG in February 2016. As of July 2022, the United States has more LNG export capacity than any other country and has exported more LNG than any other country, according to the U.S. Energy Information Administration.
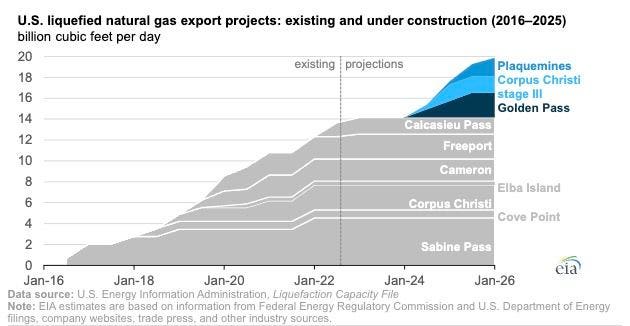
U.S. LNG export developers have finalized investment decisions (FIDs) in three expansion projects so far this year that would add about 44 million tons of LNG capacity annually. That’s nearly equal to Qatar’s mega-expansion projects. These include Venture Global’s Plaquemines LNG, Sempra’s
SRE
There is still a chance of more new projects this year as developers ride favorable winds in the global gas markets. Other potential projects in the queue include Energy Transfer’s Lake Charles LNG, Venture Global’s Calcasieu Pass 2 LNG, and New Fortress Energy’s “Fast LNG” concept.
The Ukraine war and Russia’s subsequent cutoff of piped gas to Europe have been a boon to American LNG developers. Europe, which has turned to LNG to fill the void left by Russian gas, accounted for 70% of U.S. LNG sales in 2022.
That helped the E.U. alleviate a potential gas crisis, bringing into the LNG market another huge buyer to compete with Asia. Europe last year became the world’s “premium” LNG market, paying high prices for LNG shipments, drawing them away from Asia. Buying commitments from European importers has been critical to getting new U.S. expansion projects from the drawing board to reality.
Investment in new LNG carriers since the beginning of 2022 represents 27% of total spending on new ship building and more than any other sector including containerships, according to the trade publication Seatrade Maritime. New LNG contracts placed this year total 30 carriers with a value of $7.7 billion.
U.S. producers have some key advantages in supplying global LNG markets, chiefly flexible contract terms and the competitive landscape among project developers. America’s “destination free” contracts allow LNG buyers and traders to take cargoes anywhere in the world – typically to the highest bidder where gas is most in demand – rather than limit them to a single destination.
Qatar does not offer the same flexibility. It requires firm destinations for its cargoes, a strategy that helps optimize Qatar Energy’s large shipping fleet and prevents Qatari cargoes from competing with each other on the open market.
U.S. LNG pricing models are also more favorable to many buyers. This cost-plus formula is linked to the U.S. benchmark Henry Hub gas prices, which have generally been around $2 per million Btu for years due to the vast natural gas reserves and production of America’s shale rock formations. Even with a scorching heat wave hitting the country, Henry Hub prices are still at a paltry $2.50 per MMBtu.
Qatar prefers to price LNG against the traditional oil-linked LNG benchmark, meaning its prices are exposed to the volatility of global oil markets and the whims of the OPEC cartel. That can be unsettling, especially as oil prices recently surpassed $80 a barrel again. That makes the choice easy for many LNG buyers who appreciate that U.S. LNG contracts offer more flexibility and less exposure to price risk.
The next front in the U.S.-Qatar battle will be which producer can offer the most environmentally friendly, sustainable LNG – volumes with the lowest carbon footprint. Qatar and the U.S. gas industry are taking steps to maintain a competitive edge in this area.
Qatar plans to increase its carbon-dioxide sequestration capacity to 11 million tons within a few years, which, combined with the use of solar power at its LNG plants, should give it the lowest carbon footprint in the industry globally.
However, U.S. producers are increasingly bringing in third parties to certify their natural gas emissions footprints, and a “responsibly sourced” gas movement is now in its early stages in the United States. That should help keep buyers in climate-conscious economies like Europe, South Korea, and Japan – all major LNG importers – interested in U.S. cargoes.
If analysts are correct about the return of high demand and the environmental movement continues pushing for cleaner energy options, then the United States and Qartar could both turn out to be winners.
U.S. developer NextDecade has noted that industry experts expect a global shortfall of LNG before 2030, which, if not addressed, may result in a prolonged reliance on other more carbon-intensive fuels such as coal and oil.
That means there’s ample room for the United States and Qatar to reap the benefits of the rising demand for clean natural gas.
Read the full article here