Investment Thesis
I expect Corning Incorporated (NYSE:GLW) to face challenges in 2024, particularly due to weaker optical sales and mixed demand in its display business. The anticipated recovery in the optical segment may be delayed as telecommunications customers reduce their investments and work through excess inventory. The catalysts for optical growth, such as stimulus funds, may not emerge until late 2024 or even 2025, in my view. In the long term, I still see growth potential in the Optical segment, but it is likely to be in the mid-single digits rather than the +6%-8% annual growth rate the company had previously projected, especially considering limited industry tailwinds in Automotive and Specialty Materials. Hence, I remain cautious for now and assign a hold rating to the stock.
Q3 2023 Review and Outlook
GLW missed revenue and EPS estimates in Q3 2023. The weakness in telecom spending is having a more significant negative impact on Corning’s optical sales than initially expected. This was evident in the third-quarter sales falling short of the guidance and the cautious outlook for the fourth quarter. The optical segment’s growth might continue to be challenging in the first half of the year, followed by a modest recovery in the second half of 2024. This slow recovery is due to uncertainties in telecom spending and a lack of significant catalysts like stimulus funding.
The results in the display business were mixed. While price increases supported performance, glass volumes were lower than anticipated. Corning has effectively managed its cost structure to improve margins, but it has already implemented many cost-saving measures. I believe achieving better profit growth may require more substantial cost reductions in the future.
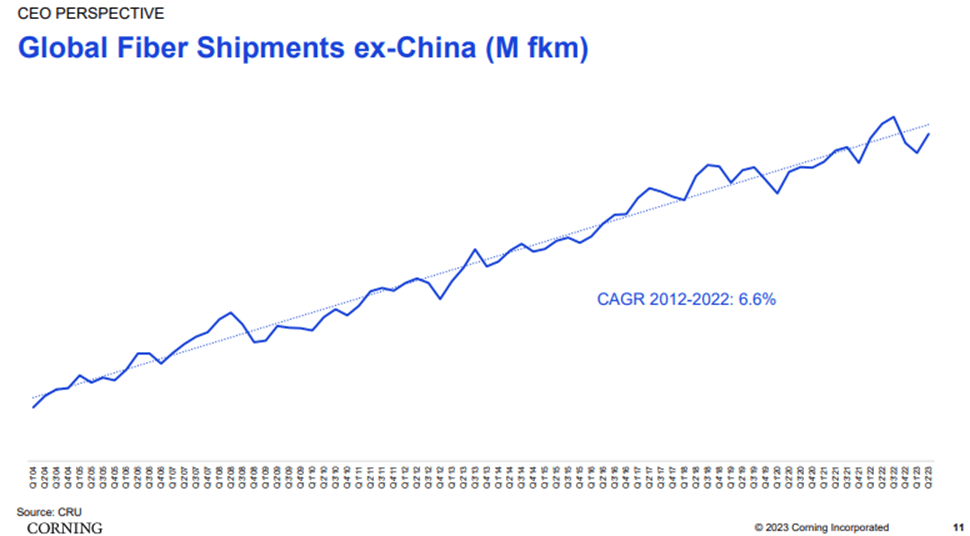
The Long-Term Need for More Fiber Is Intact
5G wireless technology and edge networks will play a significant role in increasing the density of telecommunications, broadband, and cloud networks. The unique characteristics of 5G, which operate on short wavelengths, will necessitate more small cell antennas and base stations capable of handling high data rates. According to the Fiber Broadband Association, the top 25 metropolitan areas in the United States will require 1.4 million miles of fiber cable to support a 5G network. However, Ericsson forecasts that only about 40% of the global population will have 5G coverage by 2024. In response to this competition, wireline providers are extending their fiber networks deeper into the infrastructure and closer to customers, with fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) gaining popularity. Cable companies are also adopting distributed-access architectures to remain competitive against 5G wireless services.
Looking ahead, the growing demand for data consumption is the primary driver that can sustain Corning’s optical segment. The increasing number of connected devices and the need for higher-capacity data traffic for applications like 4K video and gaming are driving the demand for faster fixed and mobile networks. These ongoing trends in data traffic are expected to drive upgrades in fiber networks and increased network density.
Corning
Financial Outlook
Corning’s manageable near-term debt load and healthy cash generation provide flexibility in its capital structure. Though the company has nearly $7 billion in gross debt ($5.7 billion net), its elongated maturity schedule helps mitigate a sense of urgency to refinance amid an unfavorable rate environment. The company has only $220 million in debt maturing in 2024-25, which it could pay off using its available cash. In 2023, Corning is expected to generate approximately $1 billion in free cash flow, and this is projected to increase by 50% in 2024, primarily driven by improved sales and profitability in its display segment. Corning also has access to a $1.5 billion credit revolver, providing a financial safety net in case of unexpected economic challenges, although such situations are not currently anticipated. Corning’s net debt-to-EBITDA ratio is approximately 2x, indicating a manageable level of debt relative to its earnings.
One of Corning’s key strengths is its operating margin in the display glass segment, which stands at around mid-20%. This is significantly higher than its competitors, with Nippon Electric Glass at 8-11% and Asahi Glass in the low single digits. Corning’s use of the fusion-glass process has helped reduce costs, enabling competitive pricing and business expansion. This advantage has translated into significant manufacturing successes, including the Gen 10.5 glass. Although Corning still faces challenges related to customer concentration that limits its pricing power, it has demonstrated the ability to pass on rising material costs to maintain its margins and mitigate inflationary pressures. Corning’s pricing actions and modest cost cuts should provide meaningful operating leverage, which could improve operating margins in the medium term.
Valuation
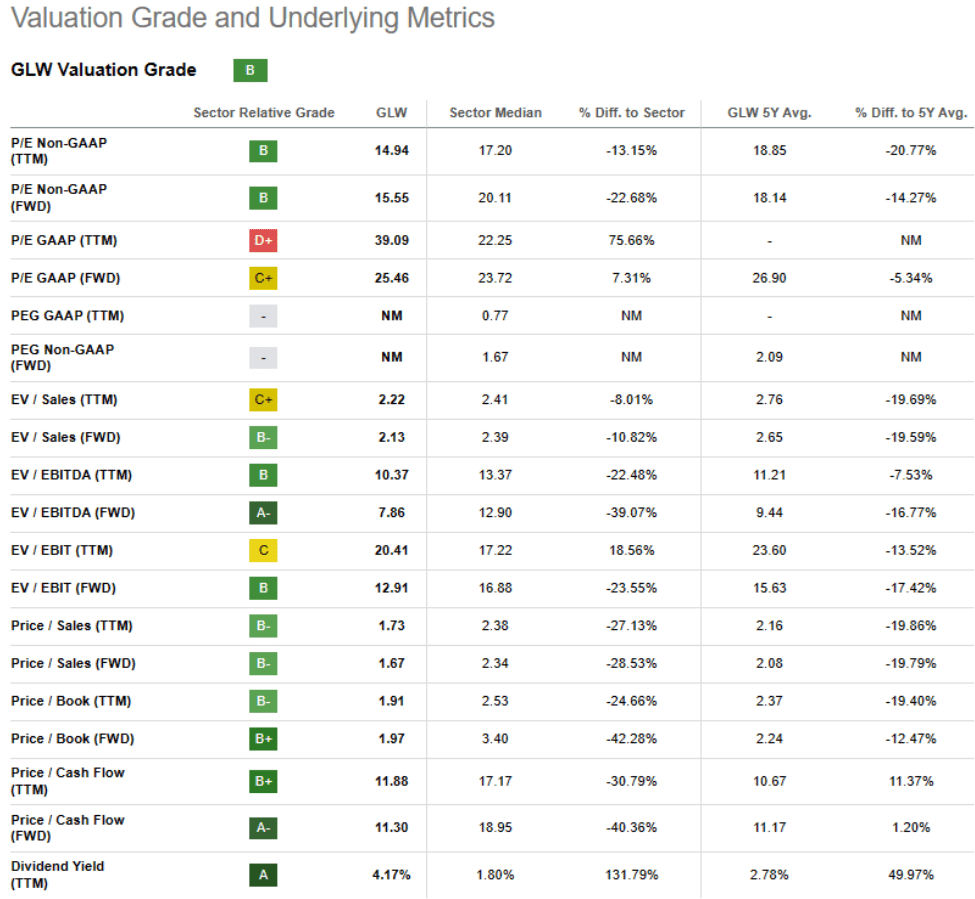
While I expect strong earnings growth in 2024, around 17% YoY, thanks to measures taken to enhance profitability (such as pricing adjustments, staff reduction, productivity enhancements, and inventory management), I believe that the varying pace of revenue recovery in different sectors Corning operates in (like Display in mid-2023, Optical probably in the second half of 2024, and uncertainty around Smartphone recovery) will limit the potential for achieving substantial earnings growth. Despite Corning’s shares trading at their 52-week lows, the implied valuation multiple of 15x next twelve months’ earnings, in line with historical multiples, offering limited upside potential. I believe recent pricing and cost adjustments should support profitability and provide some operational advantages, but the P/E ratio might remain under pressure until Corning demonstrates a sustained sales recovery. Historically, Corning’s valuation has trailed behind the S&P 500 Index, and this trend could persist due to its indirect exposure to consumer markets. Hence, I remain cautious for now and assign a hold rating to the stock.
Seeking Alpha
Investment Risks
Disruption in the current LCD and OLED display technologies poses a risk to the company. Currently, LCD displays dominate the market, followed by more expensive OLED displays. If new, less glass-intensive display technology emerges and replaces these, it could negatively impact the company. Moreover, a faster-than-expected shift to fully electric vehicles, as opposed to internal combustion engine vehicles, could hurt Corning’s earnings in its Environment Technologies segment. This segment produces substrates for catalytic converters used in emission reduction systems for internal combustion vehicles. With electric vehicles not requiring such systems, this segment’s earnings might fall short of expectations.
Conclusion
There are many growth factors driven by long-term trends, especially in segments like Optical and Solar, and the potential for expansion in consumer-oriented markets under the “more Corning” strategy. However, I have reservations due to the challenging overall economic conditions and some uncertainties in specific markets. Although certain parts of the company’s business are showing signs of improvement in the current operating environment, such as the Display sector with better utilization by panel makers and inventory levels stabilizing, there are still challenges in other areas due to issues related to demand, supply chains, or a combination of both. The company’s stock is trading in line with peers, and I assign a hold rating to the stock.
Read the full article here





